This week, the Journal of Experimental Medicine published the latest research from our Vice Dean Prof. Lu’s team. This research discovers a new regulation mechanism of Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmune inflammatory response.
The article named Suppression of Th17 cell differentiation by misshapen/NIK-related kinase MINK1 can be found on JEM Web.
Th 17 cells are a specialized subset of T helper cells capable of secreting IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22. They play important roles in maintaining intestinal health, defensing against extracellular pathogens. Th17 cells have also been identified as major contributors to many autoimmune diseases. This study demonstrates that the germinal center kinase family member MINK1 (misshapen/NIK-related kinase 1) negatively regulates Th17 cell differentiation. Moreover, direct phosphorylation at residue T324 in the α-helix 1 region and inactivation of SMAD2 were found to be the major cellular mechanism by which MINK1 modulated Th17 cell differentiation. This study further indicates that the ROS scavenger N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) markedly boost the induction of Th17 cells in a MINK1-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. In this article, antioxidant dietary supplements are proved as the risk that may result in autoimmune diseases.
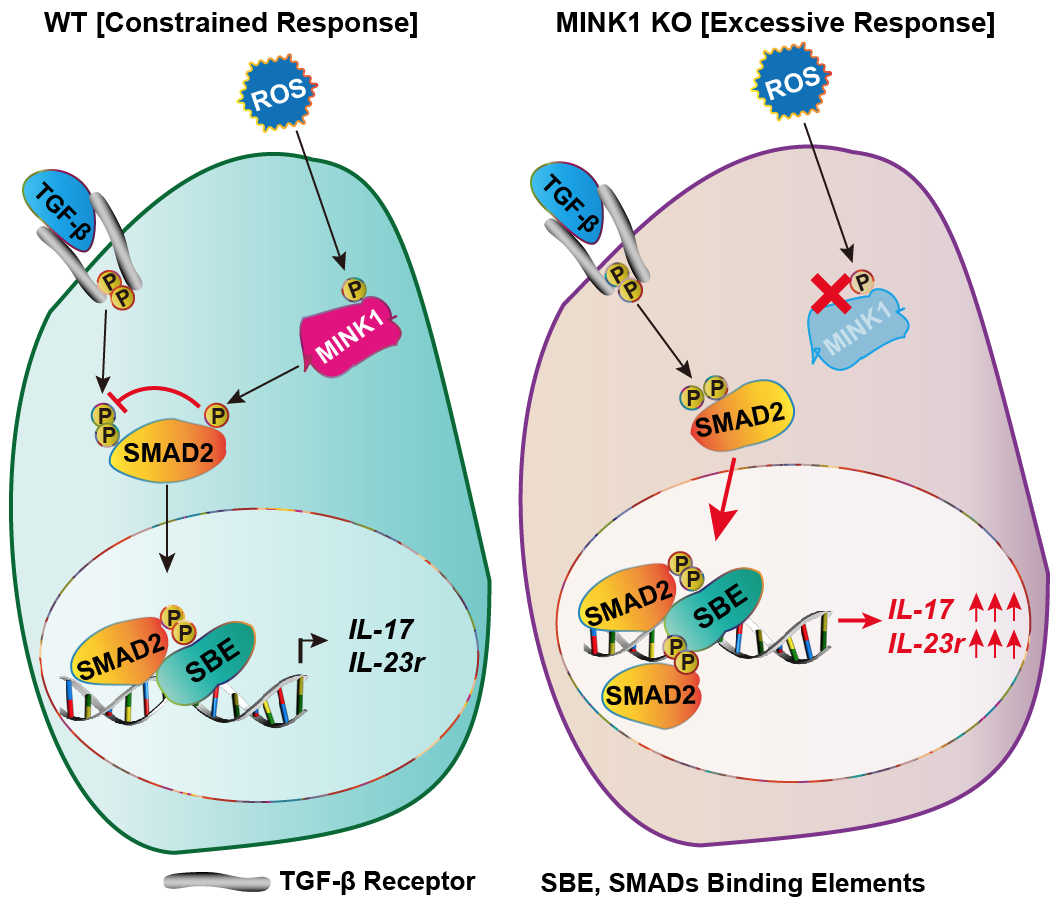
Figure. ROS suppresses Th17 cell differentiation through the activation of MINK1 kinase.
The first author of this article is Guotong Fu, Ph.D. students of Immunology, Zhejiang University. The co-authors are Qin Xu, Yuanjun Qiu, Xuexiao Jin, Ting Xu from the same research team, Prof. Harvey Cantor from Harvard Medical School, Prof. Jianli Wang and Prof. Di Wang from Institute of Immunology in Zhejiang University, Prof. Hu Hu and Prof. Yuehai Ke from Department of Pathology and Pathophysiology in Zhejiang University, Academician Prof. Xuetao Cao from National Key laboratory of Immunology, the Second Military Medical University, and Prof. Xiang Gao from Nanjing Animal Module Centre. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.







