Research Question:
T-cell receptors (TCRs) play a crucial role in the adaptive immune system by recognizing and responding to pathogens and abnormal cells. In recent years, various methods have been developed to reconstruct TCRs from single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets, each with distinct characteristics and functionalities. However, comprehensive evaluations of these methods under different conditions remain lacking. This study conducted benchmark analyses using both single-cell immune sequencing and simulated datasets, providing a benchmark study aimed at helping researchers select the appropriate method to reconstruct TCRs from scRNA-seq data.
Research Methods:
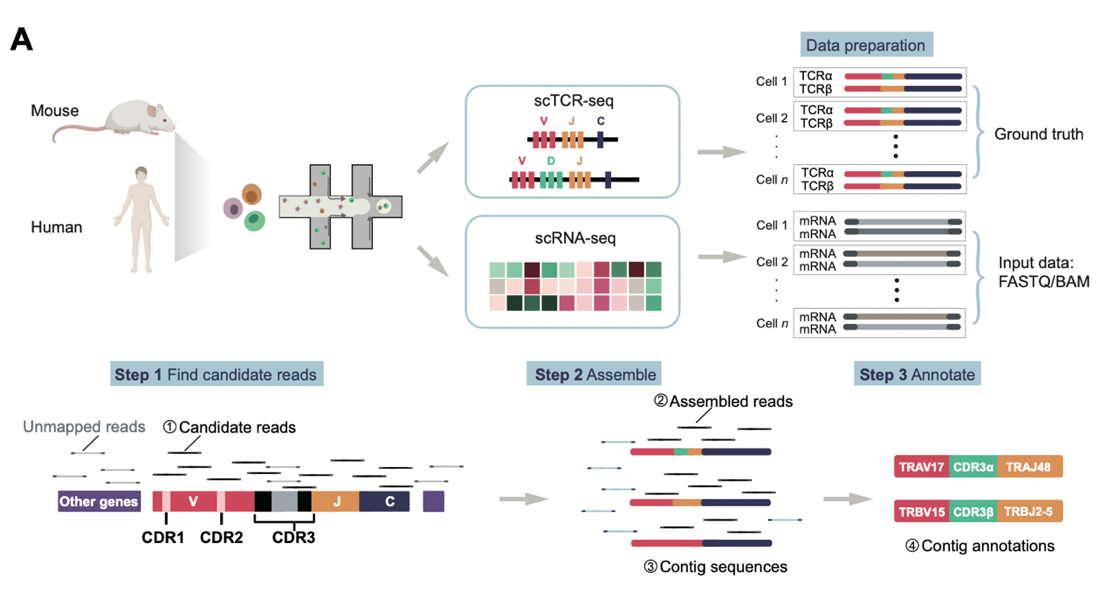
This research conducted a comprehensive performance evaluation of seven TCR reconstruction methods using multiple types of datasets, including scRNA-seq, scTCR-seq, pseudo-bulk RNA-seq, and bulk TCR-seq data. Additionally, the research team developed the YASIM-scTCR simulation tool, which generates scTCR-seq data containing TCR and non-TCR sequences based on user-defined parameters (such as sequencing depth and read length), allowing for precise comparative analysis of different methods in terms of accuracy and sensitivity. The study also provided a systematic evaluation of these seven methods in terms of sensitivity, accuracy, and computational efficiency, offering a reference for related fields.
Key Results:
In real scRNA-seq data, TRUST4 and MiXCR showed the highest sensitivity, while DeRR and MiXCR performed exceptionally well in terms of accuracy.
The YASIM-scTCR tool was developed to generate scTCR-seq simulated data containing TCR and non-TCR reads, supporting user customization of parameters such as sequencing depth and read length.
The study found that sequencing depth significantly affects TCR assembly performance in simulated data.
For pseudo-bulk RNA-seq data, TRUST4, MiXCR, and CATT outperformed other methods. In most cases, higher TCR abundance was closely associated with improved performance.
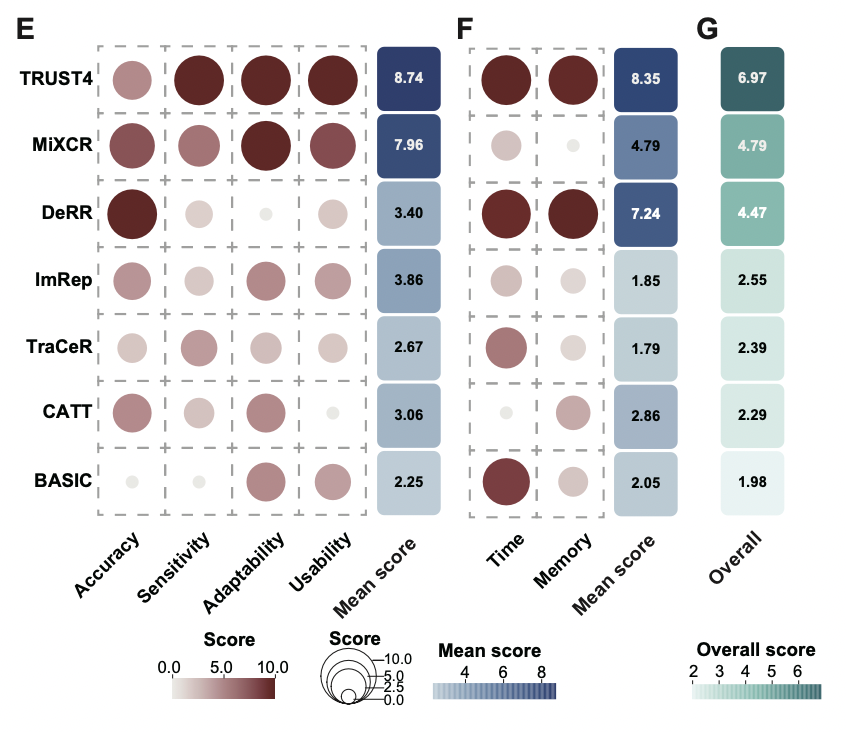
A comprehensive evaluation across six aspects—accuracy, sensitivity, adaptability, usability, runtime, and memory consumption—showed that TRUST4 ranked highest, followed by MiXCR and DeRR.
Authors and Funding Information:
Professor Liu Wanlu from ZJE is the corresponding author of this paper. PhD student Tian Ruonan and Master's student Yu Zhejian from the University of Edinburgh are co-first authors of this paper. The study involved collaboration with Tencent AI Lab’s Chief Scientist Yao Jianhua, Senior Researchers He Bing and Zhao Yu, and Professor Lu Linrong from Zhejiang University School of Medicine. Additionally, 2019 bioinformatics undergraduate student Cai Shuo from Zhejiang University actively contributed to the research. The project was supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation and the Tencent AI Lab Rhino-Bird Special Research Program.







